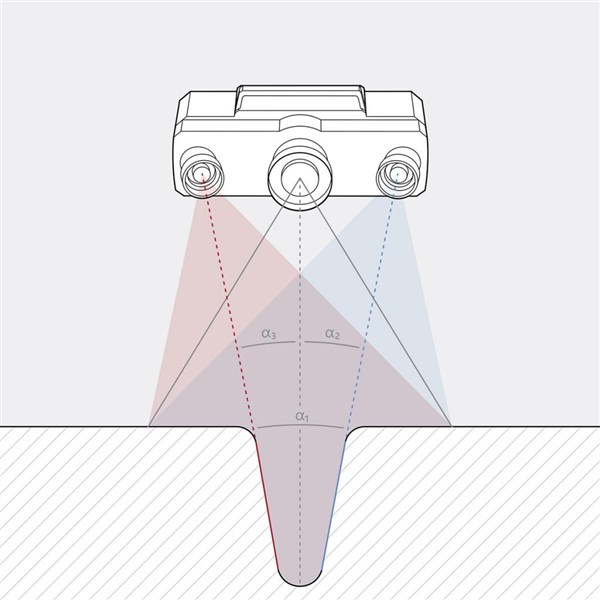
A 3D scanner is a device that collects data about the geometry (size, shape) and sometimes the color of an object, person, or surrounding environment. The output data of a 3D scanner is a set of X, Y, Z coordinate points called a point cloud, which is used to create a complete 3D model.
Dimensional measurement is how we know and quantify the size and shape of things. It involves lengths and angles as well as geometrical properties such as flatness and straightness. Dimensional measurement is of fundamental importance for interchangeability and global trade. It is how we ensure that things will fit together. Without global length standards as the basis for standardized parts globalized industry would not be possible.

From the dawn of man, there have been leaders. Even during prehistoric time, leaders walked the earth. Unlike the dinosaurs though, leaders did not become extinct.
Dimensional measurement is how we know and quantify the size and shape of things. It involves lengths and angles as well as geometrical properties such as flatness and straightness. Dimensional measurement is of fundamental importance for interchangeability and global trade. It is how we ensure that things will fit together. Without global length standards as the basis for standardized parts globalized industry would not be possible.

Dimensional Measurement allows interchangeability and global trade by ensuring things fit together
Dimensional measurement is also key to ensuring products perform as intended. For example the strength of structures is calculated using measurements such as the thickness of a flange or the span of a beam. Uncertainty in these measurements therefore increases uncertainty in the strength. This is very important for safety critical structures, for example an aircraft wing or a bridge. Another example of how measurements affect product performance is aerodynamics. If the body of a car or wing of an aircraft does not closely match the aerodynamic form which has been optimized in wind tunnel testing then the performance will not be as expected.

Dimensional metrology continues to be a key in fundamental science. For example, in particle physics, accelerator experiments currently depend on tracking detectors with sensors positioned at the micron level over 10’s of metres while the next generation light sources and high energy colliders will require highly accurate magnet positioning over 10’s of kilometres. In astronomy dimensional measurement is also critical with the most accurate optical telescopes requiring very large mirrors with sub-micron accuracy. The science of dimensional measurement is dimensional metrology, these terms are often used interchangeably.


The Gran Telescopio Canarias with a Reflector area of 74 m2 – Dimensional Measurements are used to Ensure Correct Mirror Curvature
(84) 896 555 247