The 3DeVOK MQ is a wireless color 3D scanner manufactured by Scanology. Inheriting features from industrial 3D scanners, the 3DeVOK MQ offers endless creative possibilities and is the perfect device for: 3D printing, cultural heritage preservation, reverse engineering, creative design, art, medical product design, research, and education. This makes it a suitable solution for many small and medium-sized businesses.
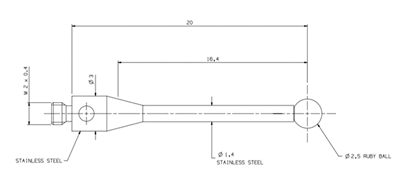
In principle, styli are the co-ordinate measuring machine’s (CMM’s) “tools”, providing the same relationship that turning tools have with lathes, and milling and boring tools have with milling machines. When measuring with a touch-trigger probe, the machine uses the stylus to take the data points on the surface of the workpiece. Each touch generates a point that is defined using co-ordinate values in X, Y and Z. Feature, size, form and position can then be computed from these points.
In principle, styli are the co-ordinate measuring machine’s (CMM’s) “tools”, providing the same relationship that turning tools have with lathes, and milling and boring tools have with milling machines. When measuring with a touch-trigger probe, the machine uses the stylus to take the data points on the surface of the workpiece. Each touch generates a point that is defined using co-ordinate values in X, Y and Z. Feature, size, form and position can then be computed from these points.
In principle, styli are the co-ordinate measuring machine’s (CMM’s) “tools”, providing the same relationship that turning tools have with lathes, and milling and boring tools have with milling machines. When measuring with a touch-trigger probe, the machine uses the stylus to take the data points on the surface of the workpiece. Each touch generates a point that is defined using co-ordinate values in X, Y and Z. Feature, size, form and position can then be computed from these points.
In principle, styli are the co-ordinate measuring machine’s (CMM’s) “tools”, providing the same relationship that turning tools have with lathes, and milling and boring tools have with milling machines. When measuring with a touch-trigger probe, the machine uses the stylus to take the data points on the surface of the workpiece. Each touch generates a point that is defined using co-ordinate values in X, Y and Z. Feature, size, form and position can then be computed from these points.
In principle, styli are the co-ordinate measuring machine’s (CMM’s) “tools”, providing the same relationship that turning tools have with lathes, and milling and boring tools have with milling machines. When measuring with a touch-trigger probe, the machine uses the stylus to take the data points on the surface of the workpiece. Each touch generates a point that is defined using co-ordinate values in X, Y and Z. Feature, size, form and position can then be computed from these points.
In principle, styli are the co-ordinate measuring machine’s (CMM’s) “tools”, providing the same relationship that turning tools have with lathes, and milling and boring tools have with milling machines. When measuring with a touch-trigger probe, the machine uses the stylus to take the data points on the surface of the workpiece. Each touch generates a point that is defined using co-ordinate values in X, Y and Z. Feature, size, form and position can then be computed from these points.
In principle, styli are the co-ordinate measuring machine’s (CMM’s) “tools”, providing the same relationship that turning tools have with lathes, and milling and boring tools have with milling machines. When measuring with a touch-trigger probe, the machine uses the stylus to take the data points on the surface of the workpiece. Each touch generates a point that is defined using co-ordinate values in X, Y and Z. Feature, size, form and position can then be computed from these points.
In principle, styli are the co-ordinate measuring machine’s (CMM’s) “tools”, providing the same relationship that turning tools have with lathes, and milling and boring tools have with milling machines. When measuring with a touch-trigger probe, the machine uses the stylus to take the data points on the surface of the workpiece. Each touch generates a point that is defined using co-ordinate values in X, Y and Z. Feature, size, form and position can then be computed from these points.
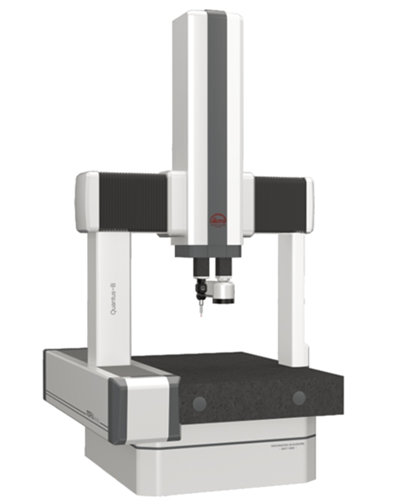
Quantus/UG - High precision and complex parts measurement solution. Read more below…
Dual Z-axis measurement solution for large, light and thin,and easily deformable parts. Read more below…
Surface evaluations using skidless tracing are needed not only in the measuring room but more and more in the production area. And MarSurf M 410 is the perfect device to do this task.
(84) 896 555 247